The history of decorative panels is a story of technological innovation, environmental adaptation, and changing design needs. This evolution has been driven by the continuous pursuit of better functionality, sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and aesthetic appeal . For professionals in the building materials industry, understanding this progression is key to appreciating the value of modern materials like PVC decorative films.
The following timeline outlines the major stages in the development of decorative panels:
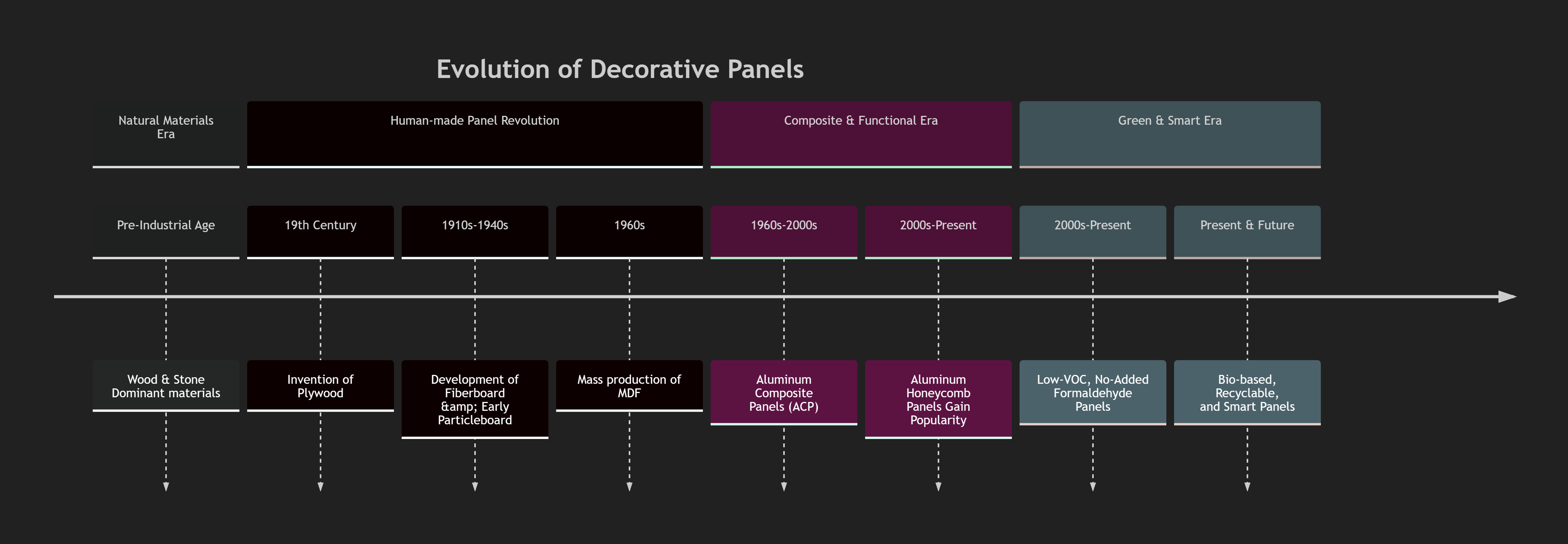
The Era of Natural Materials:
Before industrialization, decorative applications relied heavily on solid wood and natural stone. Solid wood offered natural grain and texture but was prone to warping, cracking, and insect damage. Its reliance on slow-growing timber also raised significant environmental concerns about deforestation . Natural stone, such as marble and granite, provided a luxurious and durable option but was extremely heavy, making it difficult and expensive to transport and install, especially in high-rise buildings. It is also fragile and its extraction can cause environmental damage . The limitations of these natural materials—their inconsistency, cost, and environmental impact—created a strong need for alternatives.
The Revolution of Human-Made Panels:
The development of human-made panels marked a significant shift from dependence on natural materials to engineered solutions. This era began with the ancient origins of plywood, which involved bonding thin layers of wood . The industrial revolution enabled the mass production of various panel types, fundamentally changing the industry.
Plywood: By cross-laminating wood veneers, plywood achieved greater strength and stability than solid wood, overcoming its tendency to warp or split .
Fiberboard (MDF - Medium-Density Fiberboard): Made from refined wood fibers, MDF has a smooth, uniform surface that is ideal for painting, veneering, and creating detailed decorative elements. However, it has relatively poor moisture resistance .
Particleboard (Chipboard): Utilizing wood chips and shavings bonded with resin, particleboard became a cost-effective and versatile material. Modern "solid wood particleboard" has significantly improved in quality and is widely used in ready-to-assemble furniture .
A pivotal advancement in this era was the development of surface finishing technologies. PVC decorative film emerged as a key material for laminating these engineered panels. Unlike simple adhesive films, PVC film is typically applied using vacuum lamination under heat and pressure, creating a durable bond that is resistant to peeling . This process allows panels like MDF and particleboard to mimic the appearance of wood, stone, or other designs with high durability and at a lower cost .
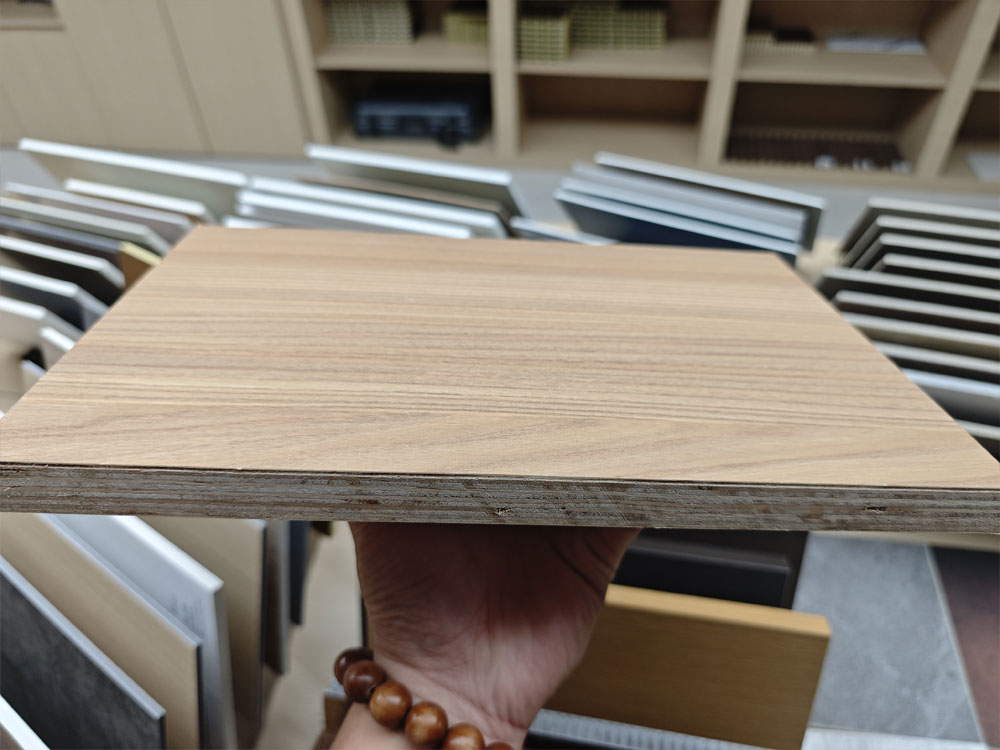

(Human-Made Panels represented by PLYWOOD)
The Era of Composites and Functionalization:
As architectural designs became more complex, demand grew for materials that were lighter, stronger, and offered additional functions. This led to the rise of metal and composite panels.
Aluminum Composite Panels (ACP): Consisting of two thin aluminum sheets bonded to a plastic core, ACPs are lightweight, flat, and come in a wide variety of colors and finishes. They are widely used for building facades and interior cladding. However, their rigidity and load-bearing capacity can be limited .
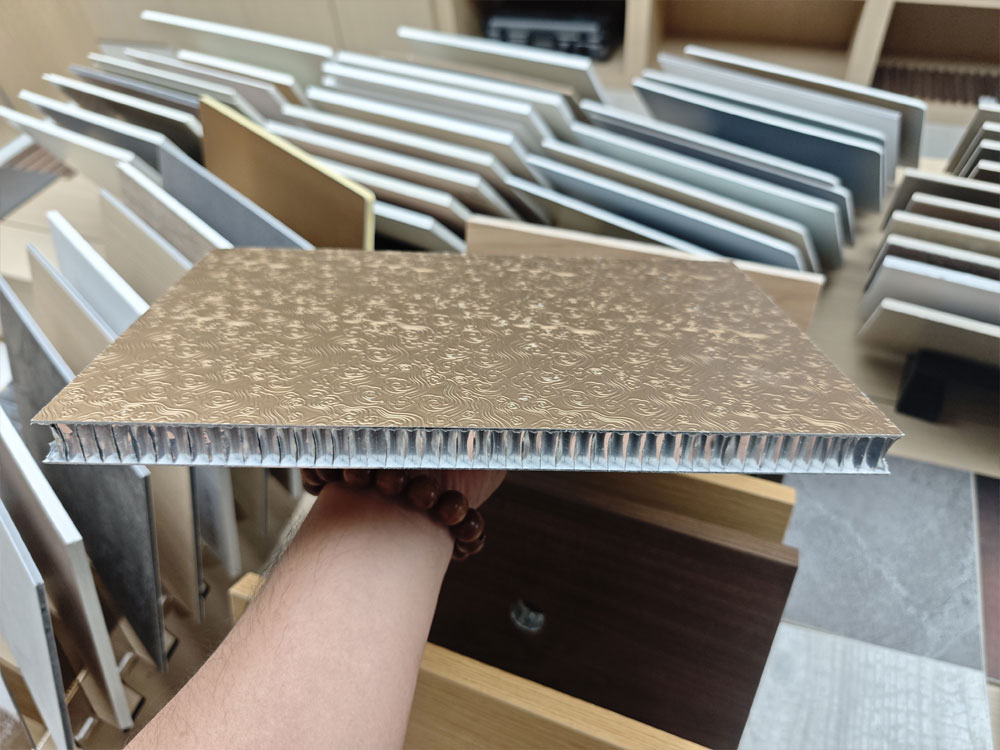
Aluminum Honeycomb Panels: This design represented a leap forward in panel technology. By sandwiching an aluminum honeycomb core between two thin aluminum sheets, these panels achieve an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. They offer excellent rigidity, flatness, and thermal and acoustic insulation properties, making them suitable for large-span ceilings, high-rise building facades, and other demanding applications .
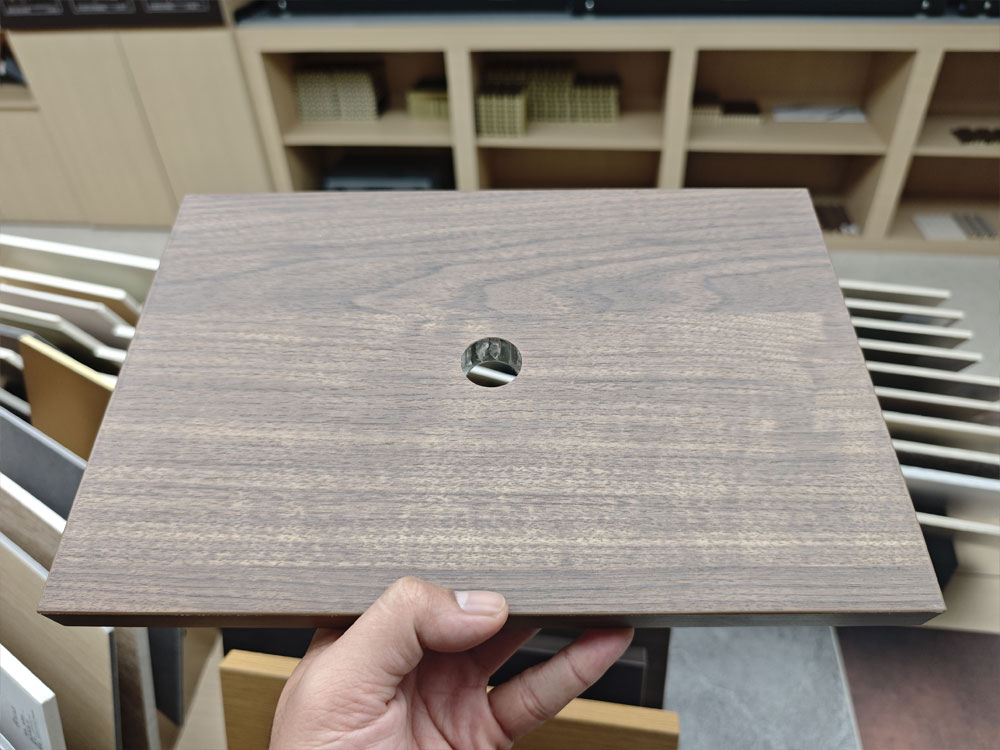

Aluminum Honeycomb Panels(with PVC decoration film)
During this period, PVC lamination technology continued to advance, allowing films to conform to the complex shapes of these new composite substrates, further expanding their decorative potential.
The Green and Intelligent Future

Today, the decorative panel industry is increasingly focused on sustainability, eco-friendliness, and smart functionality.
Green Materials: The industry has shifted toward eco-friendly production methods and adhesives. The use of MDI glue in particleboard and other panels has enabled the production of boards that meet stringent formaldehyde emission standards like "ENF" or even "non-added formaldehyde" levels . There is also a growing emphasis on using renewable materials.
Eco-friendly PVC Films: The PVC film industry is also evolving to meet higher environmental standards. This includes the use of non-phthalate plasticizers, calcium-zinc stabilizers, and the production of low-VOC emission films .
Smart and Customized Panels: The future points toward intelligent manufacturing and personalized products. PVC decorative films play a crucial role in customization, offering an vast array of colors, patterns, and textures to meet diverse aesthetic demands .
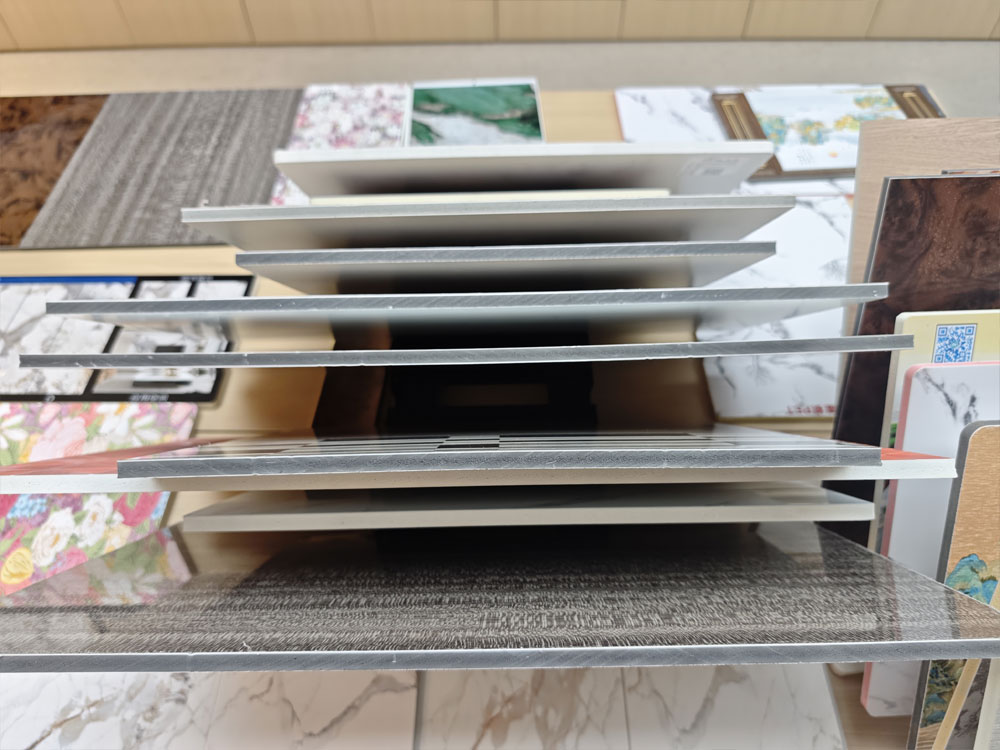

Kinds of new generation panels
As a seasoned PVC decoration film manufacturer, Team Value can recommend the most suitable film for your specific substrate choices and practical needs, fostering mutual business success.





