In the fields of interior decoration and furniture manufacturing, surface materials play a crucial role in determining a product's aesthetics, durability, and overall value. When making a selection, PVC Decoration Film and Melamine paper (also referred to as laminate or fire-resistant board surfacing) are two of the most common contenders. To assist in making a well-informed decision, we will conduct an in-depth comparative analysis of these two materials across several key dimensions.

Melamine Paper

PVC Decoration Film
I. Fundamental Differences: Flexible Film vs. Rigid Finish
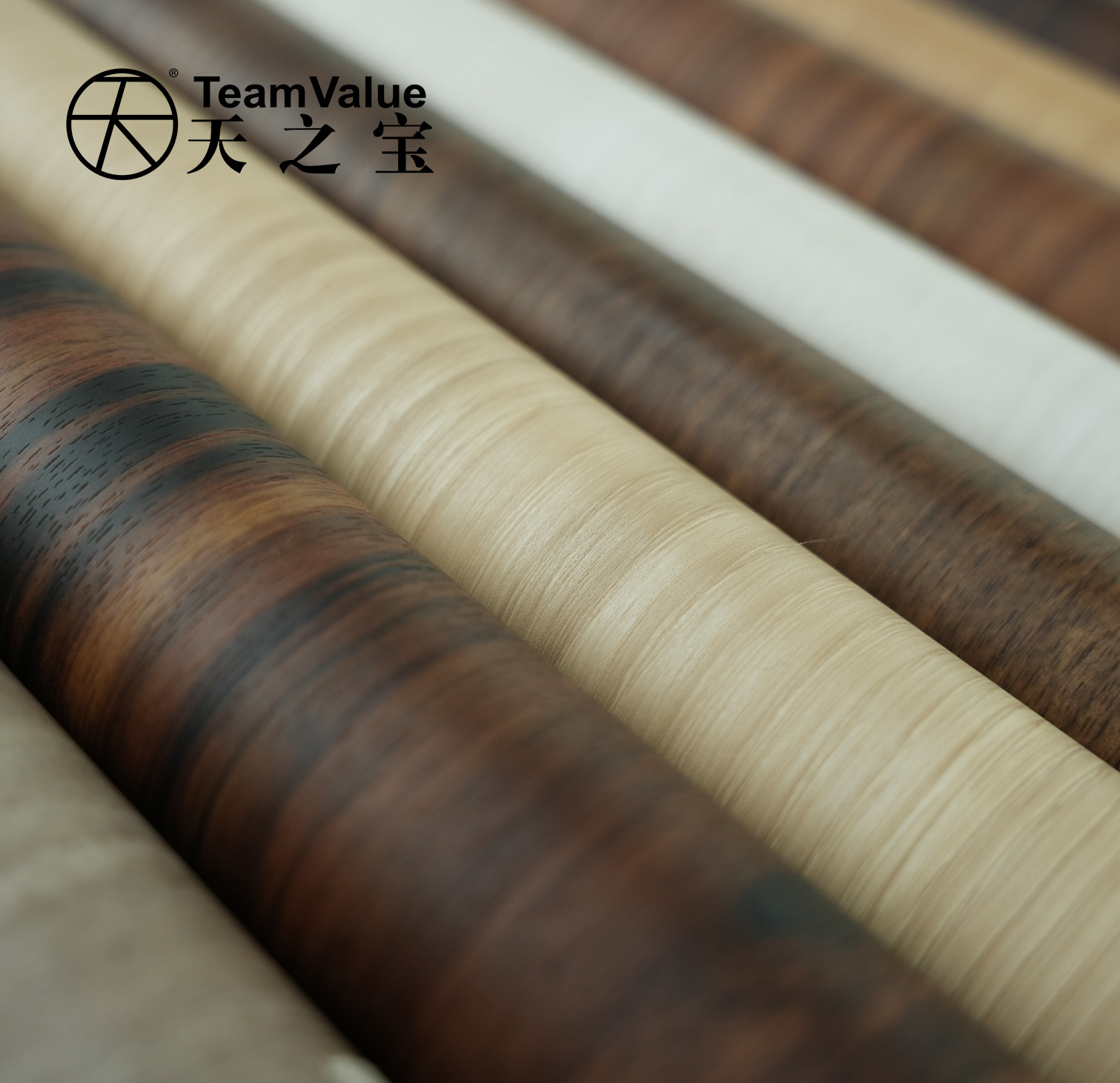
To understand their performance differences, one must start with their fundamental nature. PVC Decoration Film is a flexible composite material made primarily from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) resins and various additives. It resembles a high-quality "wallpaper" on a roll, possessing independent layers such as a wear-resistant layer, a printed pattern layer, and an adhesive backing. It can be applied to various substrates using a laminating machine. This independence grants it significant processing freedom.

Melamine Paper, fully named melamine-impregnated paper, is not an independent matrial. It involves decorative paper that is impregnated with resins (typically melamine-formaldehyde resins) and then thermally fused onto a substrate (like particleboard or MDF) under high temperature and pressure directly on the panel production line, permanently bonding with the substrate to form a single unit. Therefore, the melamine finish is more like the substrate's "native skin" and is inherently rigid .
II. Point-by-Point Comparison of Core Performance
1. Water and Moisture Resistance: Significant Advantage for PVC
In humid environments, material stability is paramount. PVC film is composed of high-molecular polymers that are completely non-absorbent, forming an excellent barrier that effectively blocks moisture and prevents substrate swelling and deformation. This makes it an ideal choice for kitchen and bathroom cabinets, laboratory countertops, and hospital wet areas . In contrast, while the surface resin of melamine paper offers some moisture resistance, its weakest point lies in the cut edges. If the edge banding becomes slightly damaged or the seam is imperfect, moisture can penetrate the substrate, leading to irreversible swelling and cracking, severely impacting the furniture's lifespan.

2. Wear, Scratch Resistance, and Durability: Toughness vs. Pure Hardness
Melamine paper has a very hard surface and performs well against everyday friction. Its weakness, however, is brittleness; it lacks flexibility and can easily sustain permanent white scratches or chips when heavily scraped by sharp objects. High-quality PVC Decoration Film, on the other hand, is often coated with a special transparent wear-resistant layer. This layer is not only hard but also possesses excellent toughness, meaning it better withstands impacts and scratches, resisting permanent marks even from minor bumps. For high-frequency, high-wear scenarios like school desks, public space furniture, and children's rooms, the toughness of PVC film offers more comprehensive protection .
3. Appearance Design and Processing Flexibility: PVC Unleashes Creativity
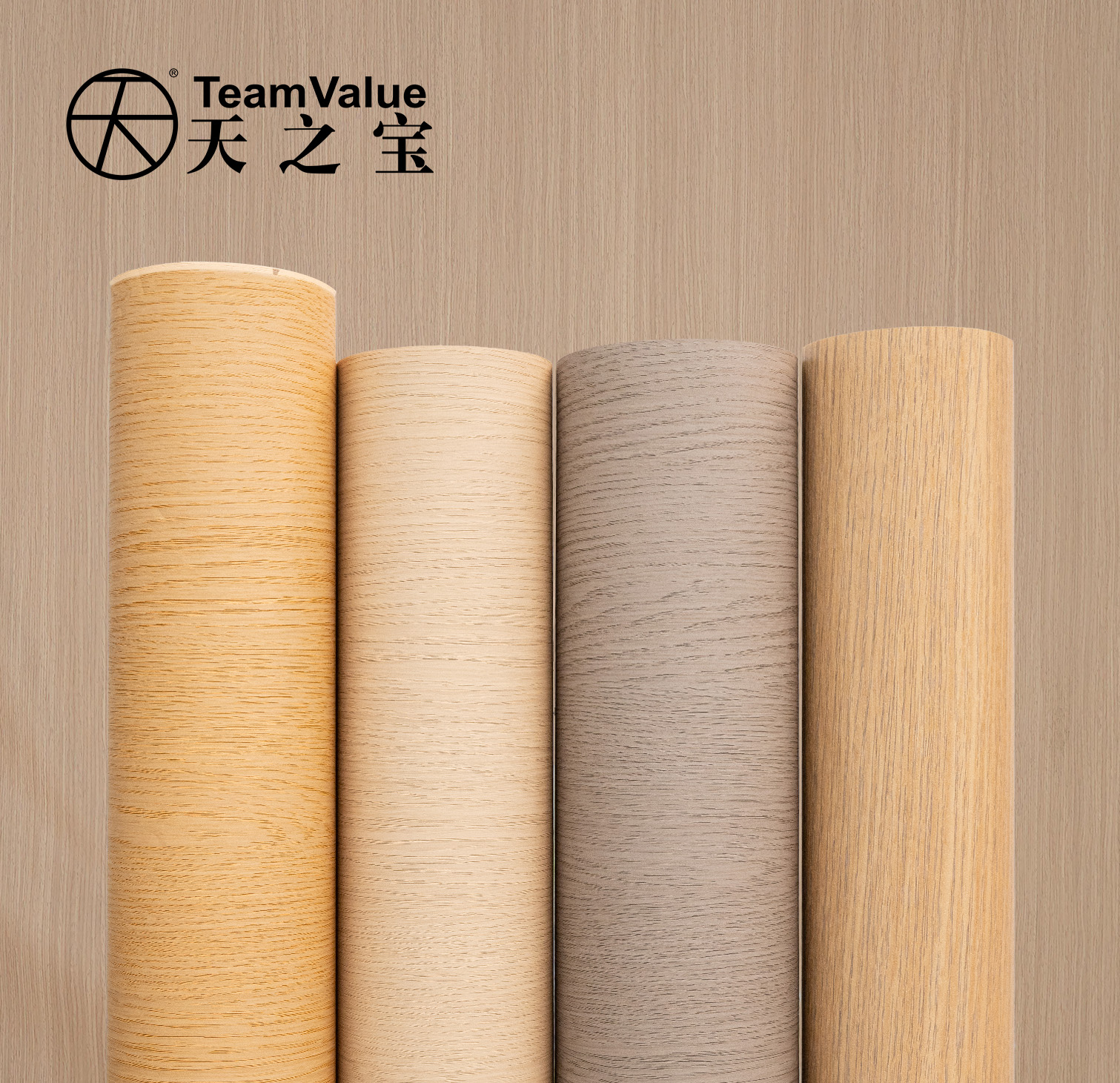
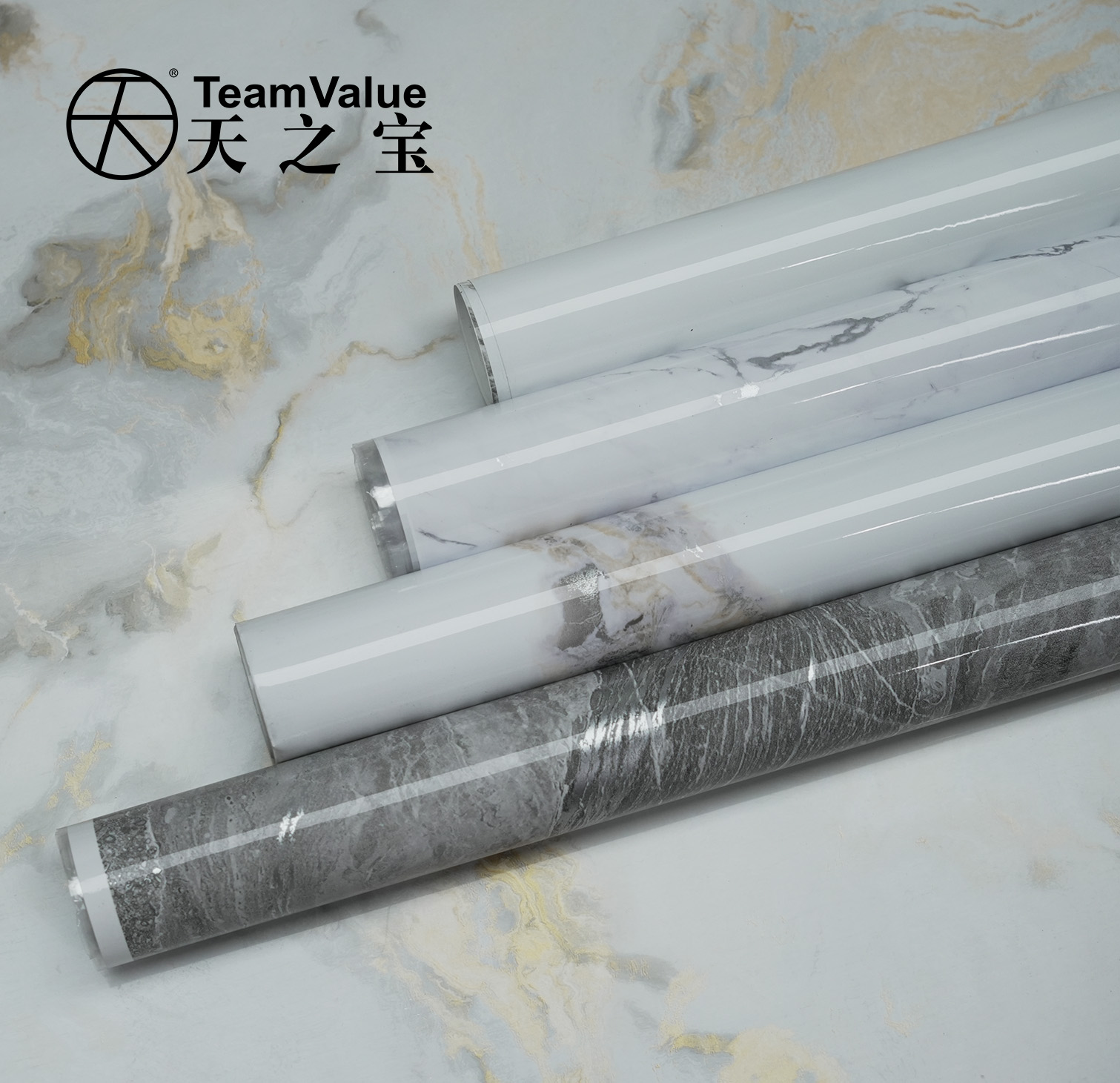
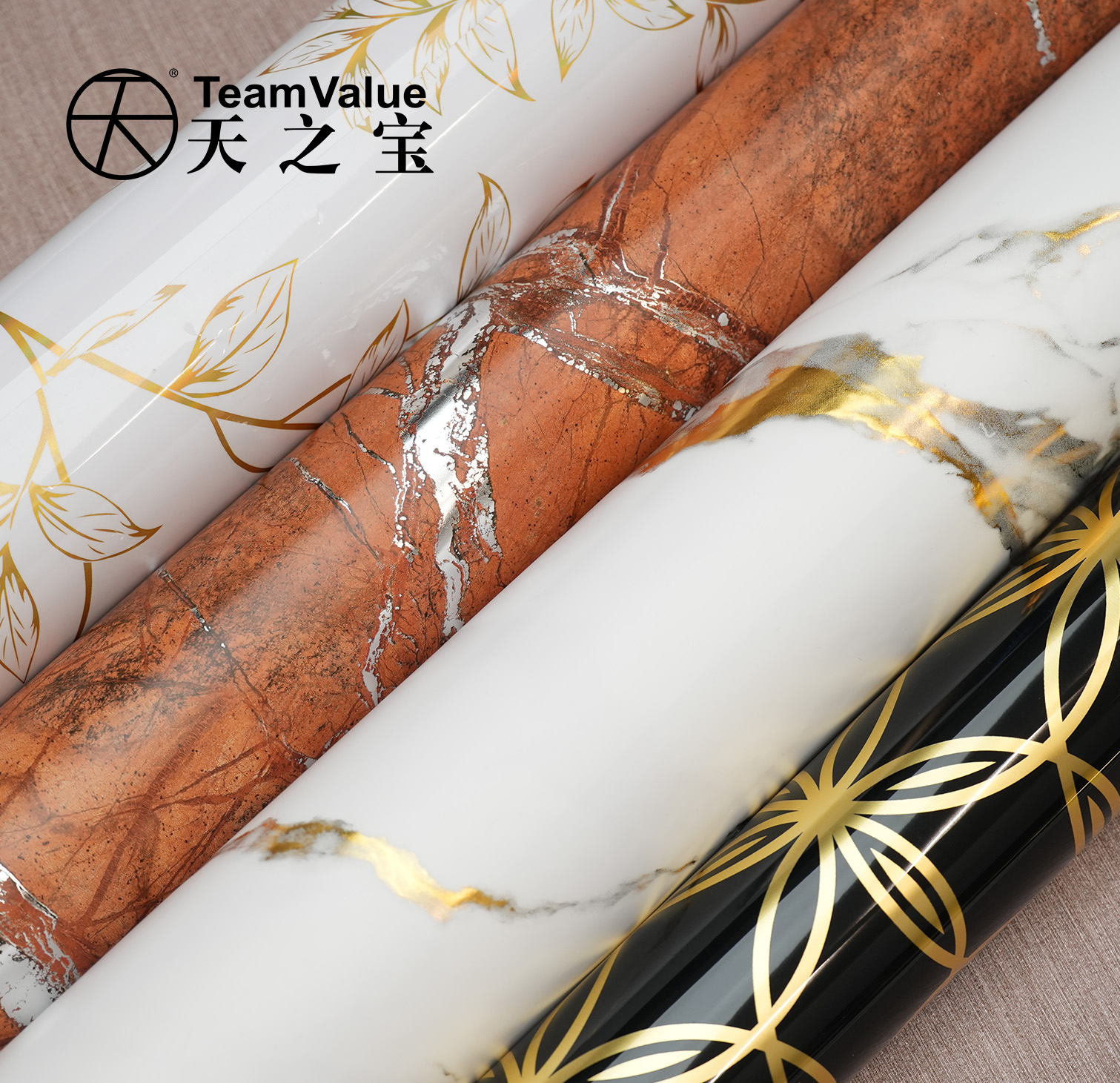
This is where PVC film significantly outperforms in value. Utilizing advanced printing and embossing technologies, PVC film can realistically mimic any wood grain, stone texture, or metallic feel, and can create rich surface textures like matte, high-gloss, soft-touch, or leather grain . Crucially, its flexibility allows it to easily wrap around edges, curves, and complex three-dimensional shapes, achieving seamless, integrated 3D effects and providing designers with broad creative possibilities . Melamine paper, by comparison, offers more traditional and limited patterns and textures, and can generally only be applied to flat surfaces, unable to handle complex three-dimensional shapes, which greatly restricts design innovation .
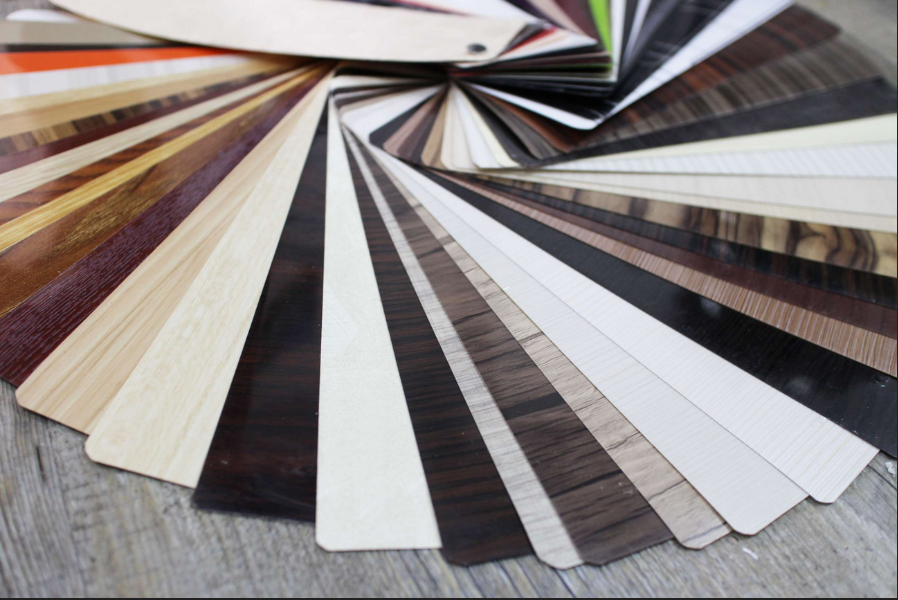

4. Processing Methods and Production Flexibility: Adapting to the Customization Era
The lamination process for PVC Decoration Film can be completed downstream at furniture factories using cold or hot adhesive laminating machines, and it is relatively forgiving regarding substrate requirements. This characteristic offers furniture manufacturers significant flexibility, enabling quick responses to small-batch, diverse custom orders – a key trend in the current market . Melamine-finished panels, however, must be surfaced during the board production stage. Furniture factories purchase pre-finished panels, limiting their processing to cutting and edge banding, with no option for secondary surfacing, resulting in lower production flexibility and being more suited for large-scale, standardized flat-panel production .

5. Environmental and Safety Considerations
Modern high-quality PVC films often use phthalate-free plasticizers and lead-free stabilizers. Look for products with low VOC content that comply with regulations like RoHS. They are generally considered chemically stable in use . Concerns for melamine paper primarily revolve around potential formaldehyde emissions from the resins, especially if they do not meet strict standards (such as E0 or CARB Phase 2). Seeking low-formaldehyde certification is important.
III. Conclusion: A Decision for the Future
In summary, melamine paper retains its place in economical, standardized flat-panel furniture applications, particularly for interior components like shelves and cabinet bodies where budget is a primary concern.
However, if your priorities include:
1. Superior performance (especially in waterproofing and abrasion resistance),
2. Leading-edge design (rich colors/patterns, complex shapes),
3 . Production flexibility (adapting to custom demands),
4 . And long-term value (high cost-effectiveness, low maintenance),
Then, PVC Decoration Film is unequivocally the superior, more future-oriented choice. It is not merely a surface material but a strategic tool for enhancing product competitiveness and capturing the high-end market.





